Ensure Your Family’s Safety Through Understanding Earthquake Hazards and Preparedness
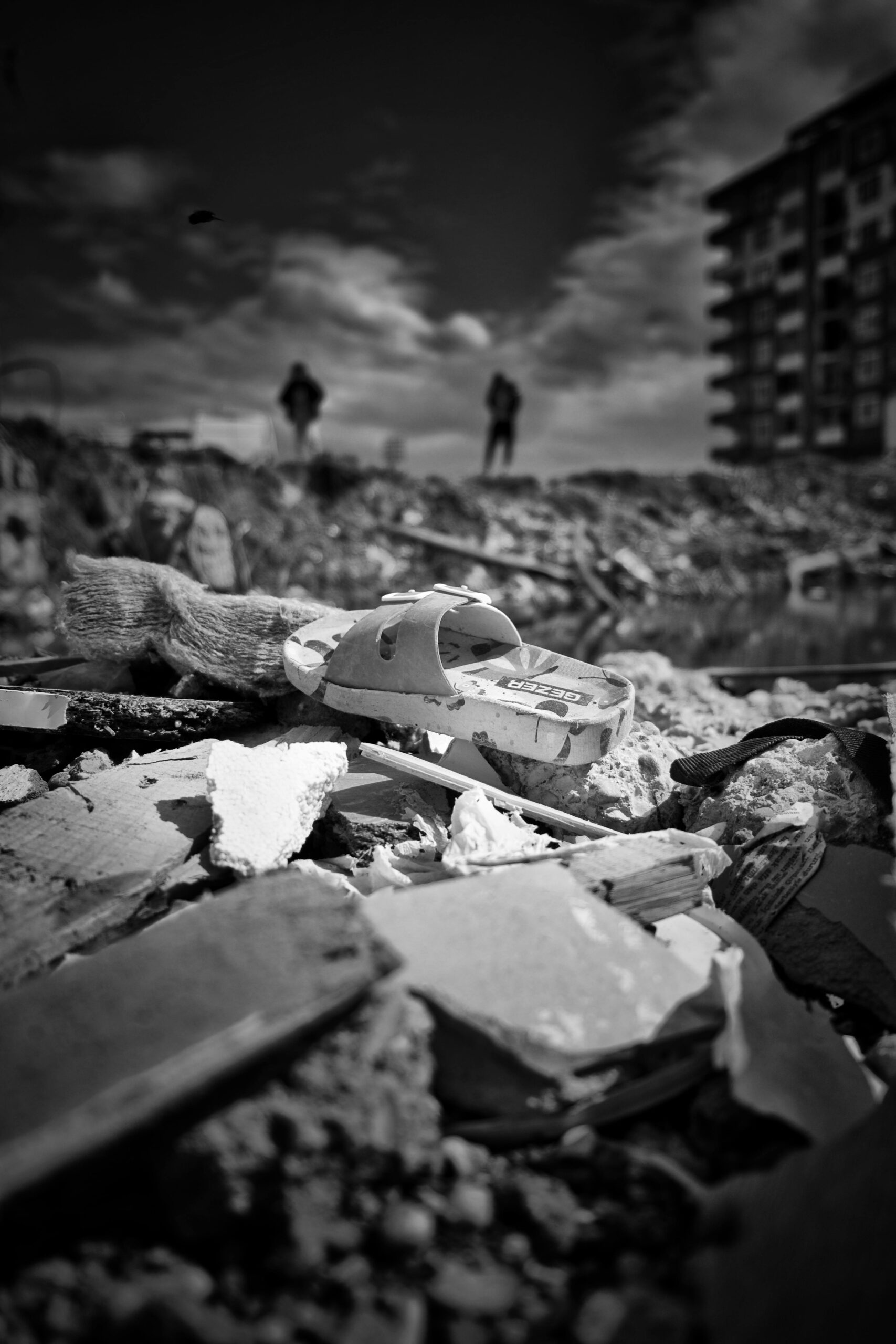
Earthquakes are natural phenomena that can cause immense destruction and pose significant risks to life and property. Understanding the hazards associated with earthquakes and how to protect oneself is crucial, especially in regions like the Philippines, which is highly susceptible to seismic activity.
.
Types of Hazards During an Earthquake
- Ground Shaking: The primary hazard during an earthquake is the violent shaking of the ground, which can cause buildings to collapse, infrastructure to fail, and the ground to crack. The intensity of ground shaking depends on the earthquake’s magnitude, depth, distance from the epicenter, and the local geological conditions.
- Surface Rupture: Earthquakes can cause the ground to split and shift along fault lines, creating visible cracks and deformations on the Earth’s surface. This can damage roads, pipelines, and buildings directly above the fault line.
- Landslides: Earthquakes can trigger landslides, especially in hilly or mountainous areas. The shaking can destabilize slopes, causing soil and rock to slide downhill, burying structures, and cutting off roads.
- Liquefaction: In areas with loose, water-saturated soils, the shaking can cause the ground to behave like a liquid. This can lead to buildings sinking, tilting, or collapsing as their foundations lose support.
- Tsunamis: Underwater earthquakes can generate massive sea waves that can inundate coastal areas. Tsunamis can travel across oceans at high speeds and cause widespread flooding and destruction upon reaching land.
- Fire: Earthquakes can rupture gas lines, damage electrical systems, and topple objects, leading to fires. With emergency services often overwhelmed, these fires can spread rapidly and cause significant damage.
How to Protect Yourself
- Before an Earthquake:
- Prepare an Emergency Kit: Include essentials like water, non-perishable food, first aid supplies, medications, flashlights, batteries, and important documents.
- Secure Your Space: Fasten heavy furniture, appliances, and electronics to walls. Use latches on cabinets and secure heavy objects that could fall and cause injury.
- Create a Family Emergency Plan: Know the safe spots in each room (under sturdy furniture, against interior walls), establish a meeting place, and practice drop, cover, and hold-on drills.
- During an Earthquake:
- Drop, Cover, and Hold On: Drop to your hands and knees, cover your head and neck, and take cover under sturdy furniture. Hold on until the shaking stops. If no shelter is available, move away from windows and exterior walls and cover your head and neck.
- Stay Indoors: If you are indoors, stay there. If you are outside, move to an open area away from buildings, trees, streetlights, and utility wires.
- If in a Vehicle: Pull over to a safe location, avoid stopping under overpasses or near buildings, and stay inside the vehicle until the shaking stops.
- After an Earthquake:
- Check for Injuries and Damage: Administer first aid if necessary and check for hazards such as gas leaks or electrical damage. Be prepared for aftershocks.
- Stay Informed: Listen to a battery-operated radio or use a mobile device to get updates and instructions from local authorities.
- Avoid Damaged Areas: Avoid damaged buildings and infrastructure, as they could collapse in aftershocks.
Earthquake Vulnerability in the Philippines
The Philippines is on the Pacific Ring of Fire, and due to multiple tectonic plate boundaries, it experiences significant seismic activity. This geographic setting makes the Philippines highly prone to earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
Notable Earthquakes in the Philippines
- 1990 Luzon Earthquake: On July 16, 1990, a magnitude 7.8 earthquake struck Luzon, causing extensive damage and over 1,600 deaths. Baguio City was particularly hard hit, with numerous buildings collapsing and landslides blocking roads.
- 2013 Bohol Earthquake: On October 15, 2013, a magnitude 7.2 earthquake struck Bohol, causing widespread destruction, including the collapse of centuries-old churches and infrastructure. Over 200 people lost their lives, and thousands were displaced.
- 2019 Cotabato Earthquakes: In October 2019, a series of strong earthquakes, the largest being 6.6, struck Cotabato and surrounding areas. These earthquakes caused significant damage to buildings and infrastructure and resulted in numerous casualties.
The Importance of Preparedness
Given the Philippines’ vulnerability to earthquakes, preparedness is not just advisable but essential. Earthquakes can strike without warning, and their impacts can be devastating. Being prepared can mean the difference between life and death. It ensures that individuals and communities can respond effectively, minimize damage, and recover more quickly.
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding earthquake hazards and taking proactive measures can significantly reduce the risks.
- Preparing an emergency kit, securing your space, and having a family emergency plan are vital steps.
- Knowing what to do during and after an earthquake can save lives and prevent injuries.
- The Philippines’ geographic location necessitates heightened readiness and resilience against seismic events.
By fostering a culture of preparedness and resilience, communities can better withstand the impacts of earthquakes and protect the lives and livelihoods of their residents.